The brain is a complex organ that operates on electrical impulses. Brainwaves, which are rhythmic electrical patterns, play a crucial role in regulating various cognitive and physiological processes. Among these brainwaves, delta waves are associated with deep sleep, emotional processing, and memory consolidation. While a balanced level of delta waves is essential for optimal brain function, both excess and low delta wave activity can have significant effects on our mental and physical well-being. In this blog post, we will explore the impact of excess and low delta waves on the brain and how neurofeedback can help in achieving the right balance.

Delta Waves: An Overview
Delta waves are the slowest brainwaves, with a frequency range of 0.5 to 4 Hz. They are predominantly observed during deep sleep stages (NREM sleep) and are characterized by high amplitude and slow oscillations. Delta waves are generated by the thalamus and neocortex working together to synchronize neural activity during restorative sleep and memory consolidation


The Effects of Excess Delta Waves
- Sleep Disorders: An excess of delta wave activity during wakefulness can lead to sleep disorders, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, insomnia, and sleep apnea. These conditions can severely impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting concentration, mood, and overall cognitive function.
- Mental Fog and Confusion: High levels of delta waves during the daytime can lead to a mental fog, making it challenging to concentrate, think clearly, or make decisions. This effect is akin to feeling drowsy or unfocused despite being awake.
- Depression and Anxiety: Excess delta wave activity has been linked to mood disorders like depression and anxiety. An imbalance in brainwave activity can disrupt the brain’s ability to regulate emotions, leading to heightened feelings of sadness, worry, and unease.
- Cognitive Impairment: An excessive dominance of delta waves during wakefulness can impair cognitive processes such as memory, learning, and problem-solving. This can hinder academic or professional performance and lead to reduced productivity.

The Effects of Low Delta Waves
- Sleep Disturbances: Insufficient delta wave activity during sleep can disrupt the natural sleep cycle, resulting in shallow or fragmented sleep. This can lead to issues like insomnia or frequent waking during the night.
- Restlessness and Hyperactivity: Low delta wave levels during wakeful states can cause restlessness and hyperactivity. Individuals may experience difficulty in relaxing or remaining calm, which can interfere with their ability to rest or focus.
- Memory and Learning Difficulties: Delta waves play a critical role in memory consolidation during sleep. Reduced delta wave activity can impair memory formation and retention, making it difficult to learn and retain new information.
- Emotional Instability: Low delta wave activity has been associated with emotional instability, irritability, and mood swings. It can contribute to a lack of emotional resilience and make coping with stress more challenging.
The Role of Neurofeedback
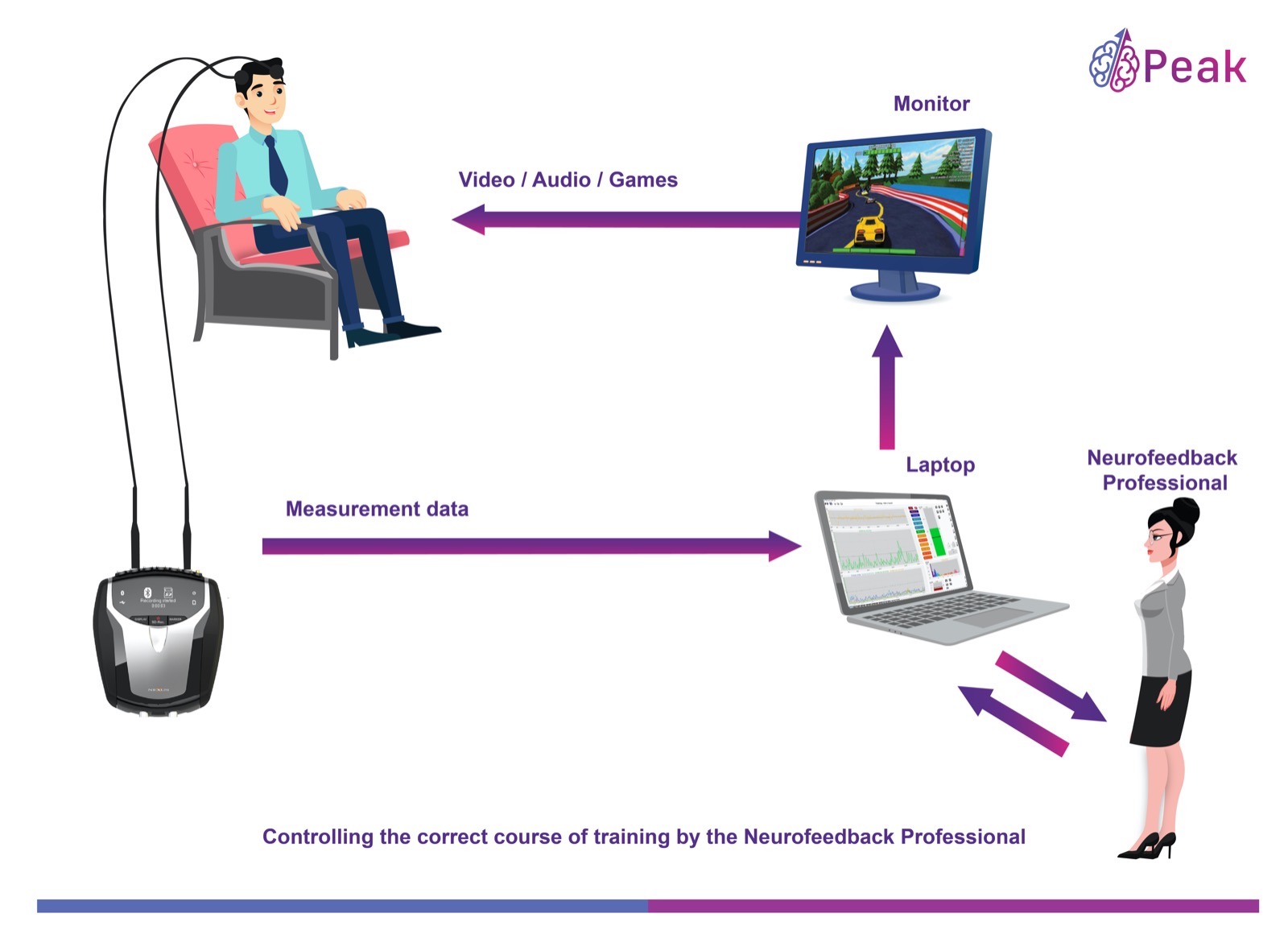
Neurofeedback is a non-invasive technique that utilizes real-time monitoring of brainwave activity to help individuals self-regulate their brain function. Through neurofeedback, individuals can gain awareness and control over their brainwaves, including delta waves. Here’s how neurofeedback can be beneficial in addressing excess and low delta wave activity:
- Balancing Delta Waves: Neurofeedback can help individuals achieve a balanced level of delta wave activity. By providing feedback on their brainwave patterns, individuals can learn to modulate their brain activity, promoting optimal levels of delta waves during appropriate times, such as during sleep or wakefulness.
- Treating Sleep Disorders: Neurofeedback can be used as a complementary approach in treating sleep disorders related to delta wave imbalances. By training the brain to produce the right amount of delta waves during sleep, individuals may experience improved sleep quality and better overall rest.
- Enhancing Cognitive Function: Neurofeedback has shown promise in enhancing cognitive abilities, including memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. By optimizing delta wave activity, neurofeedback can contribute to improved cognitive performance during waking hours.
- Managing Mood Disorders: For individuals with mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, neurofeedback can be used as a supportive therapy. By helping to regulate delta wave activity associated with emotional processing, neurofeedback may aid in emotional stability and mood regulation.
Other strategies to manage Delta waves:
- Healthy Sleep Habits: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, create a sleep-conducive environment, and avoid stimulants like caffeine before bedtime.
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Practices like meditation and mindfulness can help regulate brainwave activity, promoting relaxation and emotional stability.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, as it has been shown to positively influence brainwave patterns and improve sleep quality.
- Limit Screen Time: Reducing excessive screen time, especially before bedtime, can positively impact delta wave patterns during sleep

conclusion:
Delta waves are crucial for brain function and overall well-being. An appropriate balance of delta wave activity during wakefulness and sleep is essential for optimal cognitive performance, emotional regulation, and restorative rest. Neurofeedback is a promising technique that empowers individuals to take an active role in balancing their brainwave patterns, including delta waves. While neurofeedback can offer significant benefits, it is essential to work with trained professionals to develop a personalized neurofeedback plan tailored to individual needs. By combining neurofeedback with other healthy habits, such as proper sleep hygiene, regular exercise, and mindfulness practices, individuals can strive to achieve a harmonious brainwave balance and lead a fulfilling life.




Dear Visitors of sport.toxylact.com,
Since our launch, we have been proud to provide you with high-precision sports predictions powered by our custom-built Artificial Intelligence. However, as we look toward the future, we must make some necessary changes to how we deliver our services.
Effective March 5, 2026, we will no longer be offering free automated predictions.
To maintain the high level of accuracy you have come to expect, our system utilizes advanced Google AI Studio infrastructure. Generating these massive batches of predictions consumes approximately 20 million tokens per week. As you can imagine, the operational costs of maintaining such a powerful analytical engine are substantial, making it unsustainable to continue offering this service for free.
To ensure you can still benefit from our proven algorithm, we are pleased to offer you three ways to move forward:
1. Direct AI Interaction
You can continue to use the AI integrated into our website by manually providing the necessary data. To get an accurate forecast, you will need to input the Overall Stats for both teams, including:
• Total percentage of wins, draws, and losses.
• Average goals scored and goals conceded since the start of the championship.
2. Exclusive Online Training Course & Software Suite
For those who want to master the art of sports analytics, we are launching a comprehensive online course. We will teach you how to work successfully with our algorithm and provide you with a complete professional toolkit, including:
• Professional Bet-Tracking Software.
• Statistical Generation Software specifically designed to feed our algorithm.
• Custom Spreadsheets for all intermediate calculations.
Why choose this path? By learning to perform these analyses yourself, you gain complete independence from external providers and updates. You have the freedom to analyze any championship in the world at your own pace. Beyond the financial satisfaction of consistent results, you will find a unique sense of analytical enjoyment and intellectual growth. It transforms betting from a game of chance into a disciplined, rewarding craft.
One-time Investment: €299 (includes the full software package). How to join: Please contact us via the website’s contact form or through our integrated WhatsApp link for bank transfer details.
3. Manual Calculations
As we have always been transparent about our methodology, we have described our algorithm’s mechanics in detail within our analytical articles. If you prefer, you are welcome to take your calculator and perform the manual steps yourself to generate your own predictions.
Generating massive volumes of free, high-precision predictions is an incredibly time-consuming and expensive process. We believe these new options provide the best balance of value, education, and sustainability for our community.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.Thank you for your loyalty and understanding.
Best regards,
The Team at Lactologia Foundation
sport.toxylact.com