The human brain is a symphony of electrical activity, orchestrating our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors through various types of brainwaves. Among these, theta waves hold a significant role in our cognitive processes, emotional states, and overall mental well-being. Operating at a frequency of 4 to 8 Hz, theta waves are most commonly associated with states of deep relaxation, creativity, and even the dreamy realm between wakefulness and sleep. However, an imbalance in theta wave activity, whether excessive or too low, can lead to a range of cognitive and emotional challenges. In this blog post, we delve into the effects of excess and low theta waves on the brain and explore how neurofeedback can help in achieving a harmonious balance.

Understanding Theta Waves
Theta waves are characterized by their moderate frequency and amplitude, often linked to various mental states, including:
- Creativity and Intuition: Increased theta wave activity is often observed during moments of heightened creativity, problem-solving, and the generation of novel ideas.
- Deep Relaxation: Theta waves play a pivotal role in states of deep relaxation, such as meditation and daydreaming.
- REM Sleep and Dreams: These waves also emerge during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is the phase associated with vivid dreaming and memory consolidation.
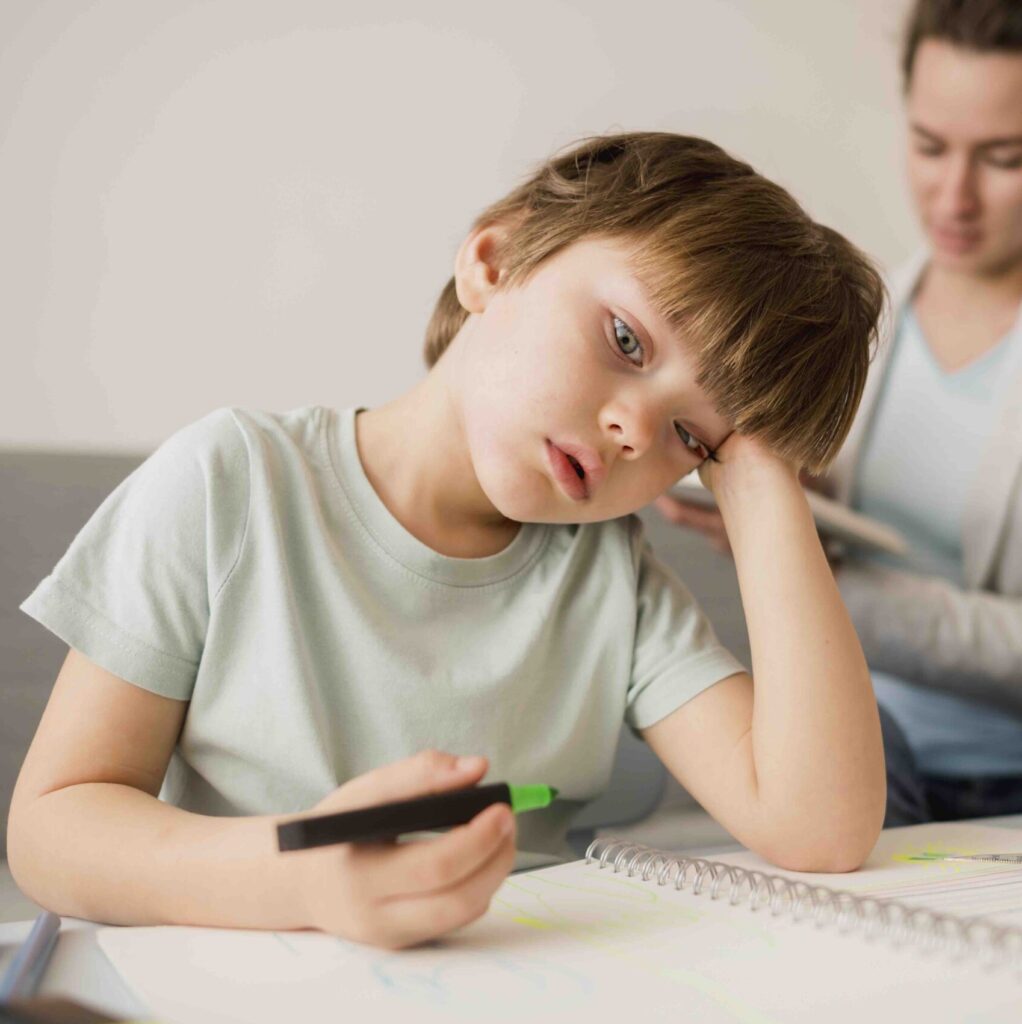


The Effects of Excess Theta Waves
- Attention and Focus Challenges: Excessive theta wave activity during waking hours can lead to difficulties in maintaining attention and focus. This can result in reduced productivity, impaired learning, and challenges in completing tasks.
- Mental Cloudiness: Too much theta activity might lead to a feeling of mental fogginess or confusion, making it challenging to think clearly or make decisions.
- Anxiety and Stress: Elevated theta wave levels have been linked to increased anxiety and stress. Individuals experiencing excess theta waves might find themselves prone to racing thoughts and a heightened sense of unease.
- Depersonalization: In some cases, an excess of theta waves can result in feelings of dissociation or depersonalization, where individuals feel disconnected from themselves or their surroundings.
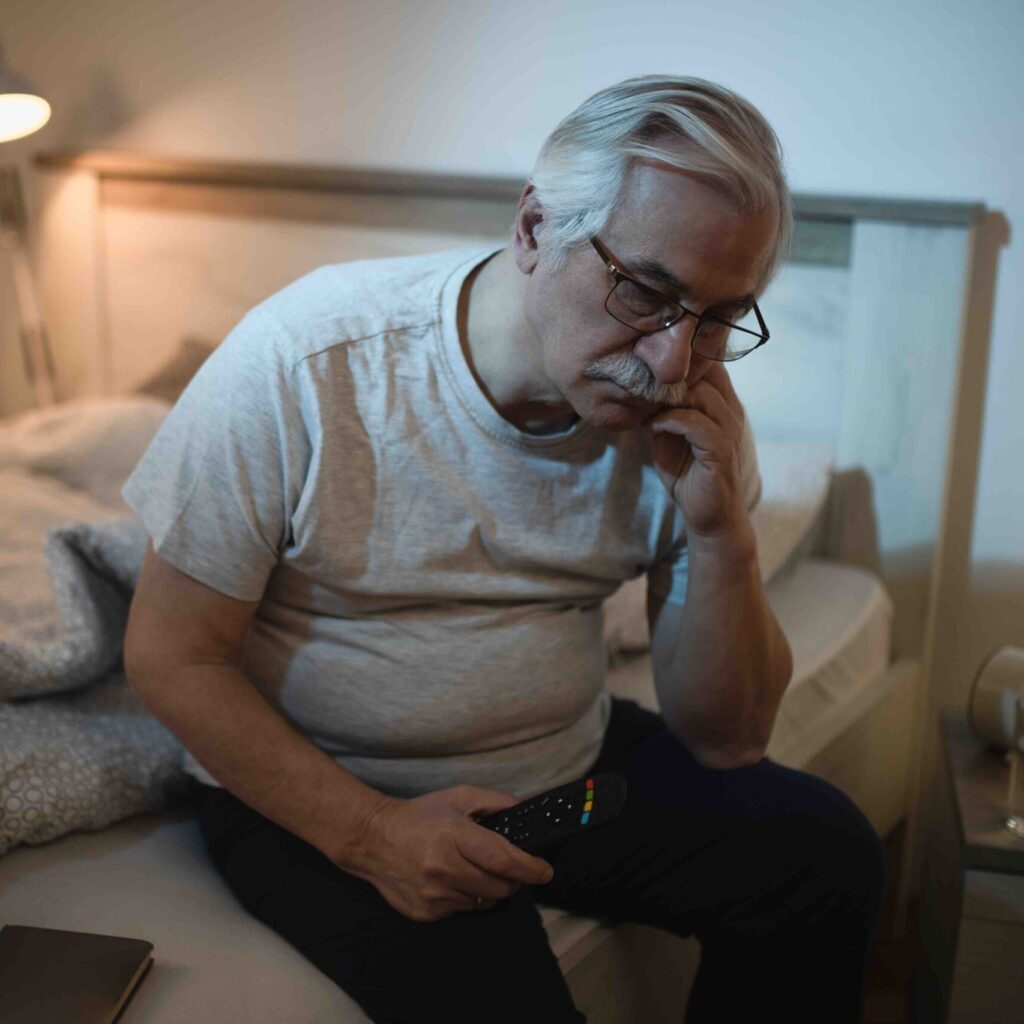

The Effects of Low Theta Waves
- Impaired Creativity: Reduced theta wave activity can lead to a decline in creative thinking, making it harder to generate innovative ideas or think outside the box.
- Memory Issues: Theta waves play a crucial role in memory consolidation and retrieval. Low theta activity may contribute to difficulties in forming new memories or accessing existing ones.
- Emotional Regulation: Healthy theta wave levels are associated with emotional regulation. Reduced theta activity might lead to mood swings, irritability, and challenges in managing emotions.
- Sleep Disturbances: Inadequate theta wave activity during REM sleep can disrupt the sleep cycle, potentially leading to sleep disturbances, reduced dream recall, and compromised memory processing during sleep.
Balancing Alpha Waves with Neurofeedback
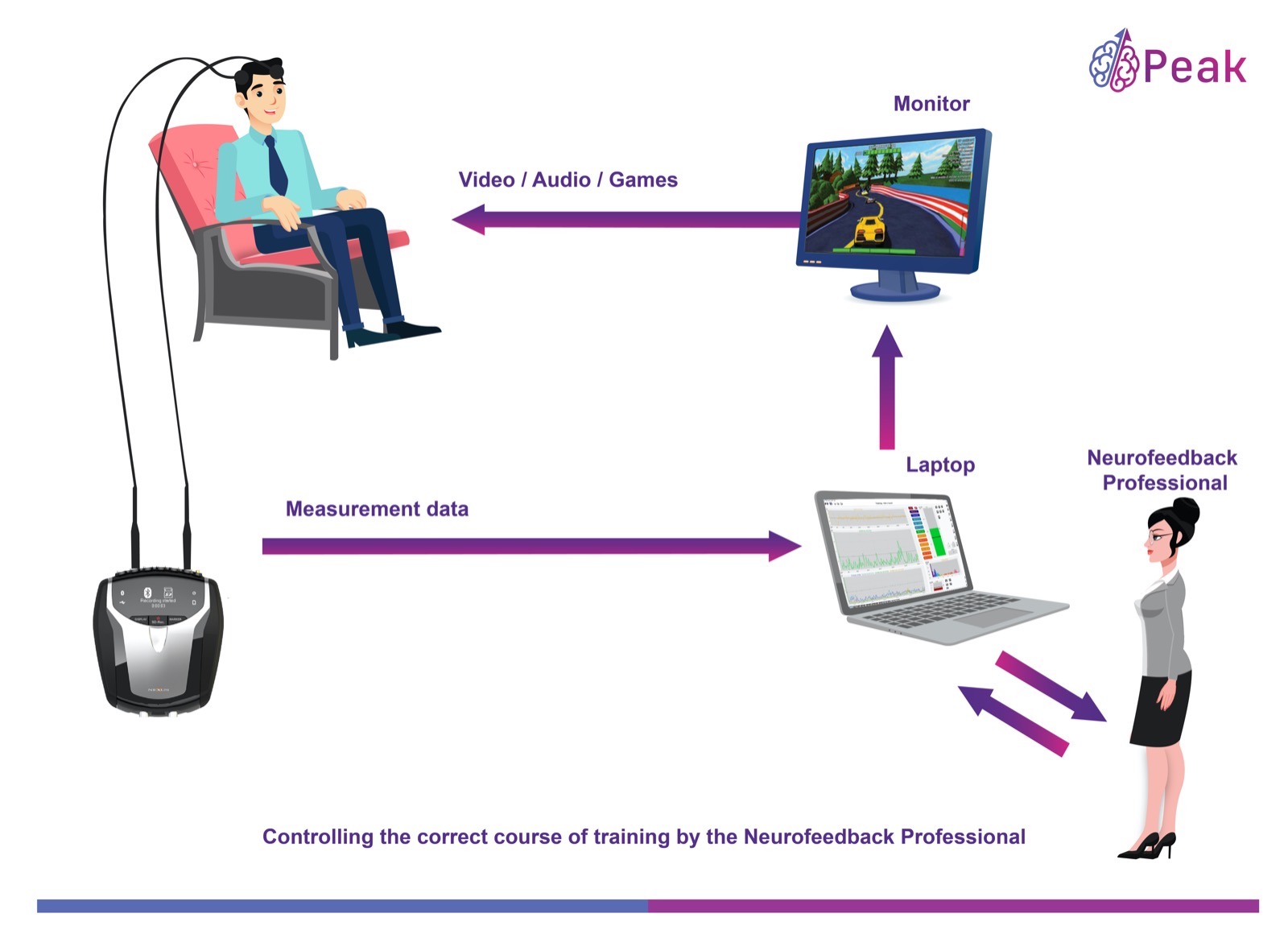
Neurofeedback is a powerful technique that empowers individuals to regulate their brainwave patterns, including theta waves, through real-time monitoring and training. Here’s how neurofeedback can play a crucial role in achieving a balanced theta wave activity:
- Awareness and Regulation: Neurofeedback provides individuals with real-time information about their brainwave activity. By observing their theta wave patterns, individuals can learn to regulate their mental states and achieve optimal theta activity.
- Customized Training: Neurofeedback sessions are tailored to each individual’s needs. Professionals can design training protocols to address specific challenges related to excess or low theta wave activity.
- Enhancing Creativity and Focus: Neurofeedback can help individuals enhance their creative thinking abilities by encouraging a balanced level of theta waves. Similarly, it can aid in improving focus and attention by regulating excessive theta activity.
- Emotional Balance: Through neurofeedback, individuals can work on achieving emotional stability by finding the right balance of theta wave activity, promoting better emotional regulation.
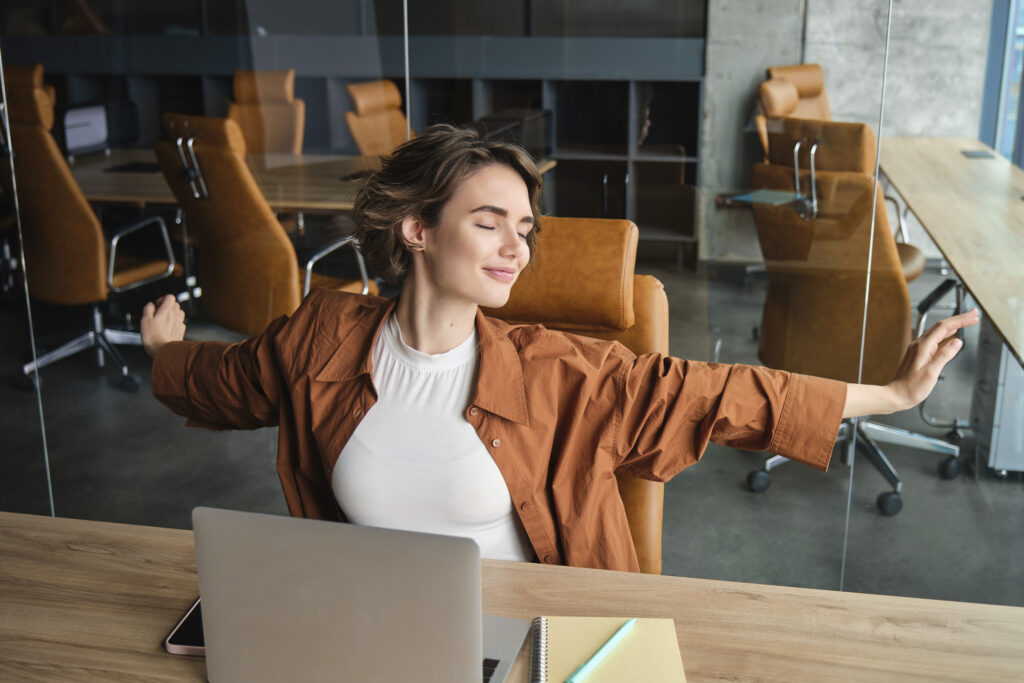

conclusion:
Theta waves offer us a fascinating glimpse into the intricate workings of the human brain. Striking the right balance of theta wave activity is crucial for optimal cognitive performance, emotional stability, and creative thinking. Neurofeedback stands as a powerful tool in achieving this balance, enabling us to influence our brainwave patterns positively. By understanding the effects of excess and low theta waves and leveraging neurofeedback, we can take proactive steps to nurture our brain health and lead more fulfilling lives. If you’re considering neurofeedback, seek guidance from trained professionals to ensure a personalized approach that aligns with your specific needs and goals.



