In the realm of mental health diagnosis, advancements in technology have paved the way for innovative approaches to understanding and assessing brain function. One such breakthrough is quantitative electroencephalography (QEEG), a non-invasive technique that measures and analyzes electrical activity in the brain. In this blog post, we will explore the applications and benefits of QEEG in mental health diagnosis, shedding light on how this powerful tool is revolutionizing the field and helping clinicians make more accurate and personalized treatment decisions.
Understanding QEEG:
QEEG involves recording and analyzing the electrical signals emitted by the brain through the use of specialized sensors placed on the scalp. These signals are then transformed into quantitative data, providing detailed information about the brain’s electrical activity. By examining various frequency bands and patterns, clinicians can gain insights into the brain’s functioning and identify potential abnormalities, dysregulation associated with different mental health conditions, or potential improvements for peak Performance.

Objective and Personalized Diagnosis:
One of the primary advantages of QEEG is its ability to provide objective data for mental health diagnosis. Unlike traditional diagnostic methods that rely on subjective assessments, QEEG offers quantifiable measurements, reducing the potential for bias and enhancing diagnostic accuracy. This objective information enables clinicians to tailor treatment plans to individual patients, ensuring a more personalized and targeted approach.
Identifying Biomarkers:
QEEG has the potential to identify specific brainwave patterns or biomarkers associated with various mental health disorders. These biomarkers can serve as valuable indicators, aiding in the identification and differentiation of different conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, anxiety disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By analyzing the unique brainwave signatures associated with these disorders, clinicians can make more precise diagnoses and develop more effective treatment strategies.
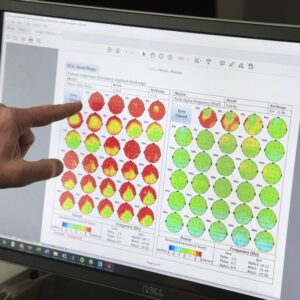

Treatment Planning and Monitoring:
QEEG not only aids in diagnosis but also plays a crucial role in treatment planning and monitoring. By examining baseline brainwave patterns and comparing them to subsequent assessments, clinicians can track the effectiveness of interventions and make adjustments as needed. This real-time feedback allows for more targeted and evidence-based treatment decisions, leading to improved outcomes and enhanced patient care.
Advancements in Neurofeedback:
QEEG findings often guide the implementation of neurofeedback, a therapeutic technique that uses real-time visual or auditory feedback to train individuals to self-regulate their brainwave activity. By incorporating QEEG data into neurofeedback sessions, clinicians can provide individuals with specific insights into their brain functioning and help them learn techniques to optimize brainwave patterns. This personalized approach promotes self-awareness and empowers patients to actively participate in their own mental health treatment.


In conclusion:
QEEG represents a significant advancement in mental health diagnosis, providing clinicians with objective and personalized information about brain function. By identifying biomarkers, tailoring treatment plans, and monitoring progress over time, QEEG enhances diagnostic accuracy and supports more targeted interventions. With the integration of QEEG into Neurofeedback and other therapeutic modalities, individuals can actively engage in their treatment journey and achieve improved mental well-being. As technology continues to evolve, QEEG holds immense promise for unlocking the mysteries of the human brain and revolutionizing mental health care.



