The human brain operates as a symphony of electrical activity, with different types of brainwaves playing distinct roles in our cognitive and emotional experiences. Beta waves, oscillating at a frequency of 12 to 30 Hz, are among these crucial brainwave types. They are closely associated with our alertness, focus, problem-solving abilities, and overall mental functioning. However, an imbalance in beta wave activity, whether excessive or deficient, can have profound effects on our mental well-being and productivity. In this blog post, we will delve into the effects of excess and low beta waves on the brain and explore how neurofeedback can play a pivotal role in achieving an optimal balance.
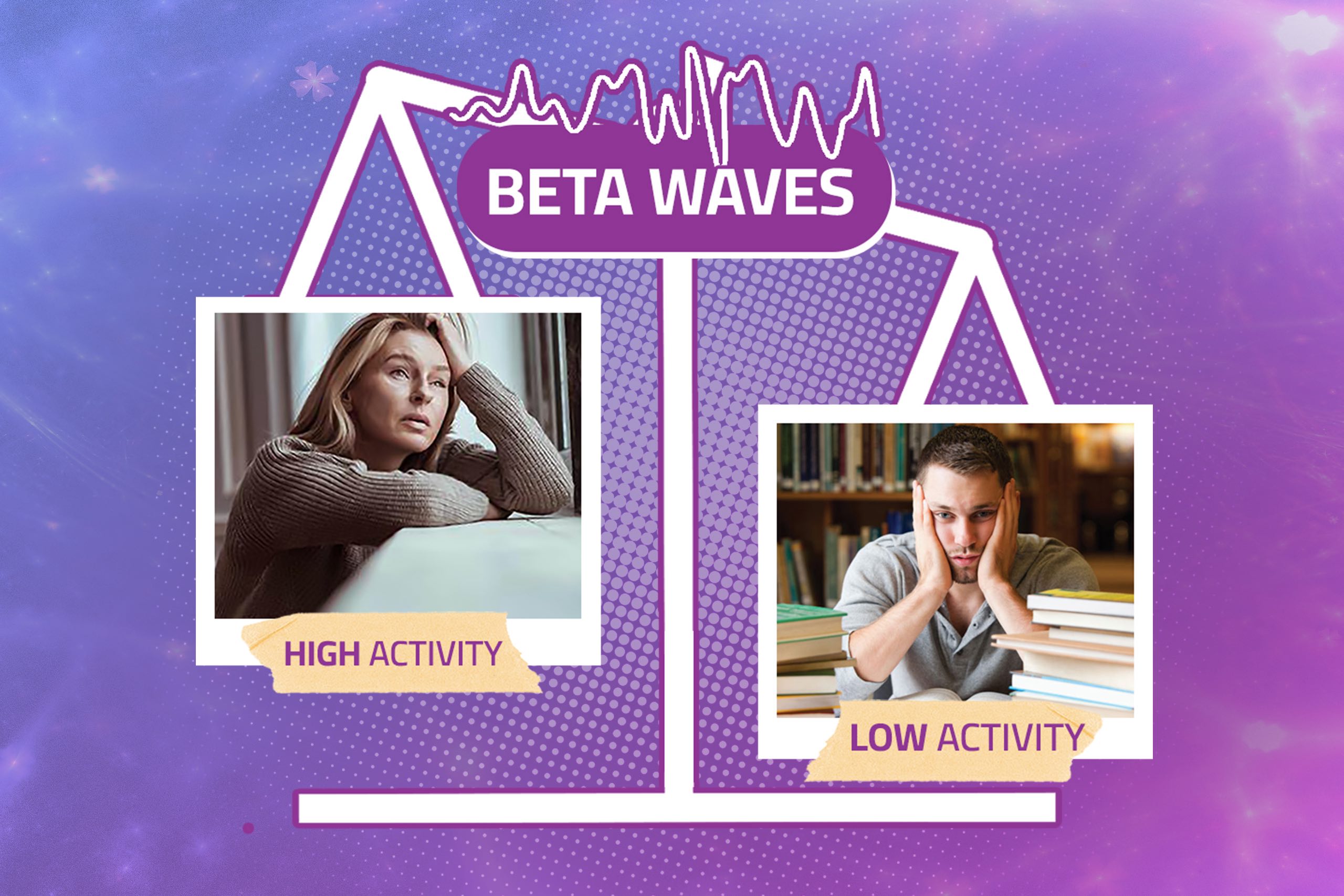
Beta Waves: A Closer Look
Beta waves are a type of neural oscillation that typically dominate our brain activity during wakefulness and periods of active mental engagement. They are often categorized into three subgroups:
- Low Beta (12-15 Hz): Associated with relaxed alertness and a calm, focused state of mind.
- Mid Beta (15-20 Hz): Linked to active problem-solving, logical thinking, and analytical reasoning.
- High Beta (20-30 Hz): Seen during states of high mental activity, such as intense concentration or anxiety.
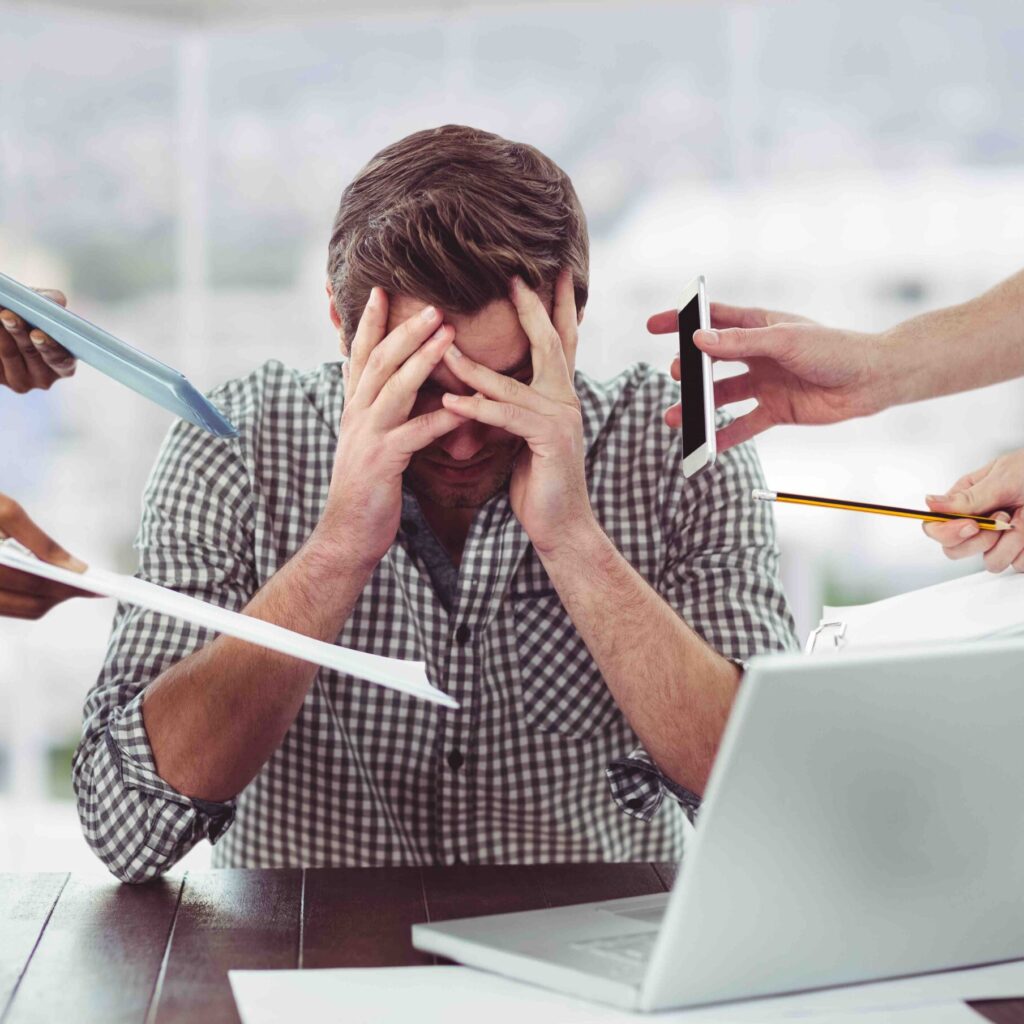


The Effects of Excess Beta Waves
- Anxiety and Stress: Excessive high-beta wave activity, especially in the range of 20-30 Hz, is often associated with anxiety and chronic stress. This can result in racing thoughts, restlessness, and a constant sense of urgency.
- Overthinking: Too much beta activity, particularly in the mid and high-beta ranges, can lead to overthinking, making it difficult to relax or let go of worrisome thoughts.
- Insomnia: An excess of beta waves, especially when it continues into bedtime, can lead to difficulties in falling asleep and maintaining restful sleep.
- Reduced Creativity: Excessive beta wave dominance may hinder creative thinking, as the mind tends to remain fixated on logical and analytical processes.
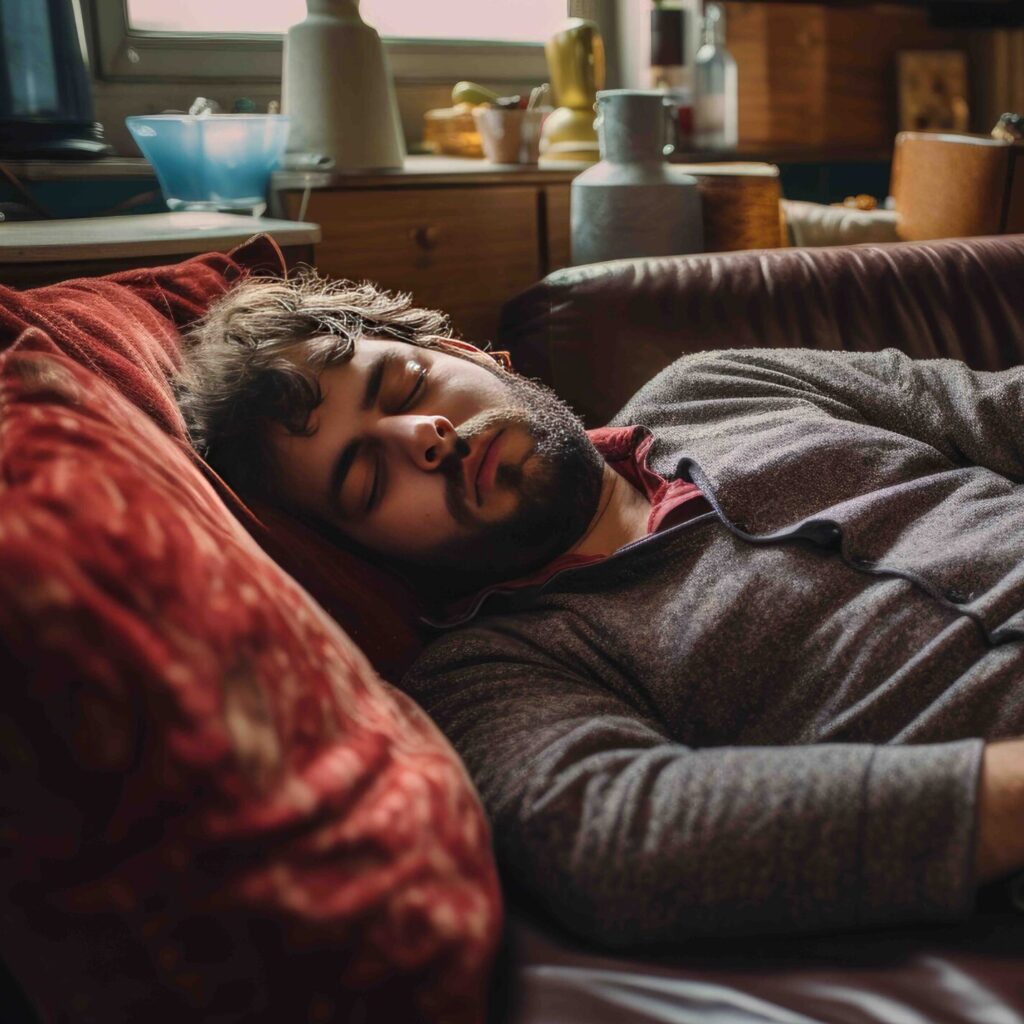

The Effects of Low Beta Waves
- Lack of Focus: Low beta wave levels can result in difficulties in maintaining focus and attention. This can lead to reduced productivity and hindered cognitive performance.
- Impaired Problem-Solving: Deficient beta activity can hinder logical and analytical thinking, making it challenging to solve complex problems or make decisions.
- Lethargy and Fatigue: Low beta wave activity can contribute to feelings of lethargy and overall mental fatigue, impacting daily activities.
- Hyperactivity: In some cases, low beta wave levels may be associated with symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Balancing Beta Waves with Neurofeedback
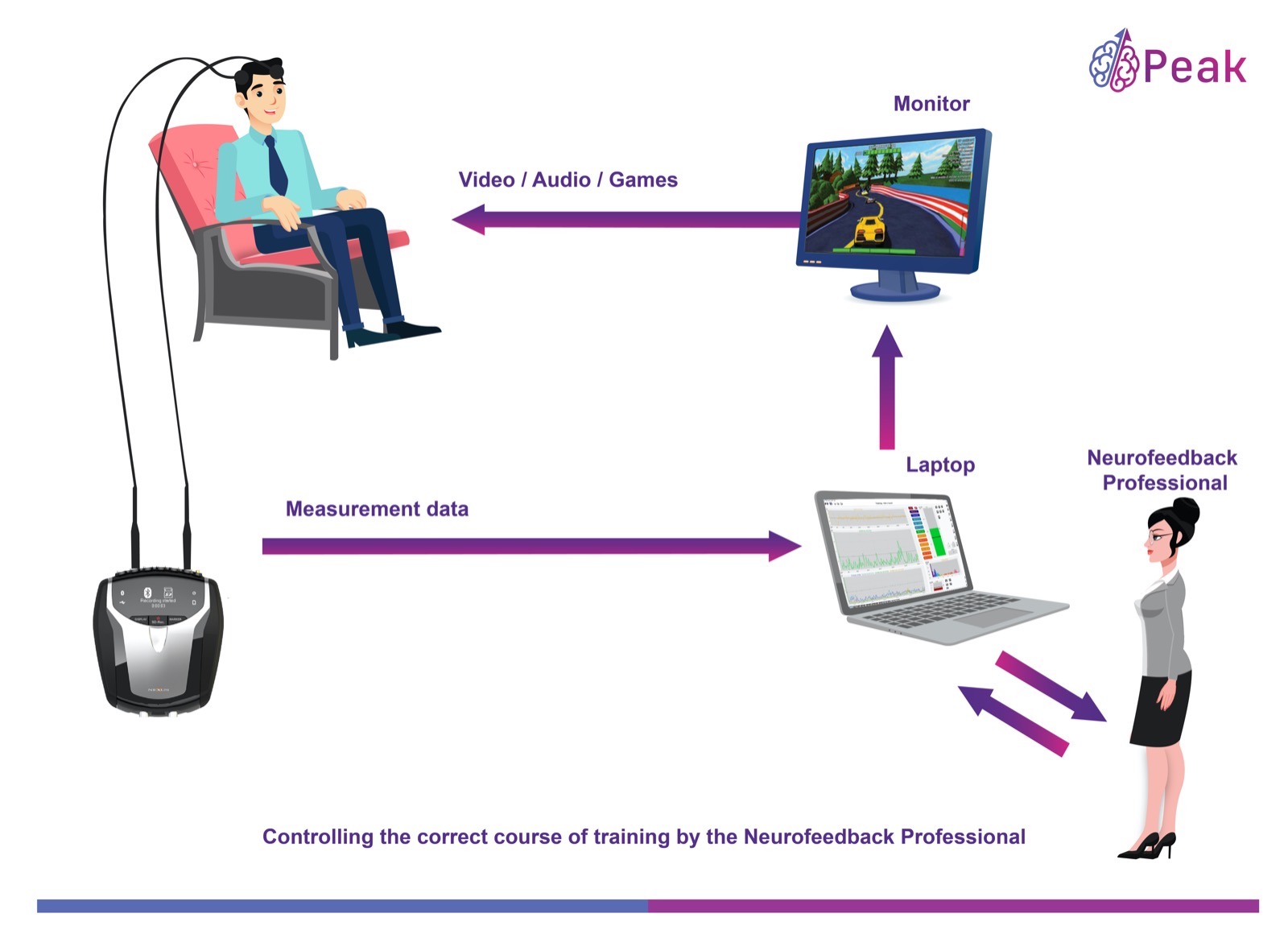
Neurofeedback is a powerful technique that enables individuals to regulate their brainwave patterns, including beta waves, through real-time monitoring and training. Here’s how neurofeedback can be instrumental in achieving a harmonious balance of beta wave activity:
- Real-Time Awareness: Neurofeedback provides individuals with real-time feedback on their beta wave activity. This awareness helps them identify when their beta waves are either excessive or deficient.
- Customized Training: Professionals can design personalized neurofeedback protocols to address specific issues related to beta wave imbalance. Whether it’s reducing excess beta waves during anxious moments or boosting beta activity for improved focus, the training can be tailored to individual needs.
- Anxiety and Stress Management: For individuals experiencing anxiety and stress due to excess beta wave activity, neurofeedback can help regulate beta waves associated with relaxation and calmness.
- Enhancing Focus and Productivity: Neurofeedback can aid in improving focus and cognitive performance by encouraging the right balance of beta wave activity during tasks that require concentration.

conclusion:
Beta waves are essential for our mental alertness, focus, and problem-solving abilities. Achieving the right balance of beta wave activity is crucial for maintaining mental well-being and cognitive function. Whether you’re dealing with excess or low beta waves, neurofeedback offers a potent tool to regain equilibrium in your brainwave patterns. By understanding the effects of beta wave imbalances and exploring neurofeedback as a solution, you can take proactive steps to nurture your brain health and lead a more fulfilling life. If you’re considering neurofeedback, it’s advisable to consult with trained professionals who can develop a personalized approach to address your specific needs and goals.



